Decimal Range Branch
The Decimal Range Branch block is a crucial element in the Range Condition category of the GraphLinq IDE. This block allows developers to define and evaluate numeric ranges for decimal values, enabling conditional branching based on whether a given value falls within the specified range.
Inputs
Value: The "Value" input represents the decimal value that will be evaluated to determine whether it lies within the defined range.
Lower Bound: The "Lower Bound" input defines the lower limit of the range. Any value greater than or equal to this lower bound is considered within the range.
Upper Bound: The "Upper Bound" input defines the upper limit of the range. Any value less than or equal to this upper bound is considered within the range.
Behavior
The Decimal Range Branch block evaluates the "Value" against the defined range using the "Lower Bound" and "Upper Bound" inputs. The branching behavior is as follows:
If the "Value" is greater than or equal to the "Lower Bound" and less than or equal to the "Upper Bound," the graph will follow the path connected to the "Within Range" output.
If the "Value" is outside the defined range, the graph will follow the path connected to the "Outside Range" output.
Example
Let's consider an example where we use the Decimal Range Branch block to check whether the temperature value falls within the "Comfortable Range" for a thermostat control system. We define the "Comfortable Range" as 20 to 25 degrees Celsius.
If the temperature reading is 22 degrees Celsius, it falls within the defined range, and the graph will follow the path connected to the "Within Range" output. This may trigger actions to maintain the current temperature.
If the temperature reading is 18 degrees Celsius, it is outside the defined range, and the graph will follow the path connected to the "Outside Range" output. This may trigger actions to adjust the temperature to bring it within the desired range.
The Decimal Range Branch block provides a versatile tool for developers to implement range-based conditions in their GraphLinq graphs. By defining specific ranges for decimal values, developers can create dynamic and responsive applications that adapt to varying data inputs and make decisions based on precise conditions. This block adds a new layer of complexity and flexibility to graphs, enabling them to handle a wide range of scenarios with accuracy and efficiency.
More Information
Decimal Range Branch blocks are used to control executive flow (which yellow connection will fire next) based upon whether a given decimal value is above (or equal to) the upper bound of a range, or below (or equal to) the lower bound of a range.
Decimal Range Branch blocks have three inputs, all of type decimal: "Value" is the number that we are checking against the range, "RangeMax" defines the upper bound of the range, and "RangeMin" defines the lower bound of the range.
If "Value" is greater than or equal to "RangeMax", then the first executive connection will fire. If "Value" is less than or equal to "RangeMin", then the second executive connection will fire.
Note that if "Value" is inside the range defined by "RangeMin" and "RangeMax", then nothing will happen. Decimal Range Branch blocks are only for detecting when "Value" is outside the range.
In the following example, we use a Decimal Range Branch block to send a message to a Telegram channel if the price of ADA goes above $2.00 or below $1.00:
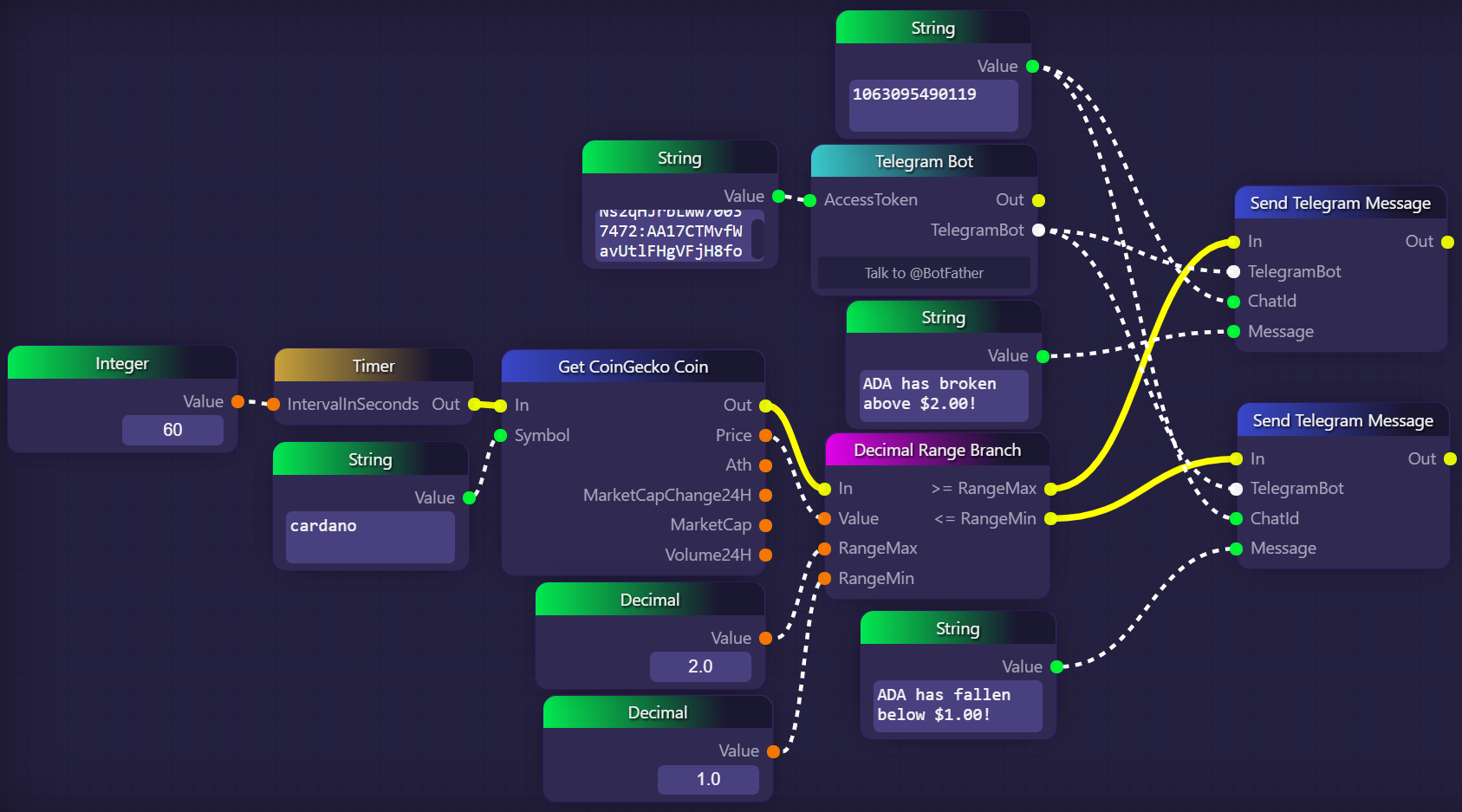
The example above is driven by the Timer block, which fires every 60 seconds. When the Timer block fires, it triggers the Get CoinGecko Coin block, which retrieves the present price of ADA. This price is then passed to our Decimal Range Branch block, which compares it to the range $1.00 - $2.00.
If the price is above the upper bound, then our Telegram bot will send the message "ADA has broken above $2.00!" to our Telegram channel using a Send Telegram Messageblock and a Telegram Bot block. If the price is below the lower bound, then our Telegram bot will send the message "ADA has fallen below $1.00!" to our Telegram channel.
If the price of ADA is inside the range, then the flow of execution will end at the Decimal Range Branch block, and our graph will wait for the Timer block to fire again a minute later.
Last updated
