Integer Branch
The Integer Branch blocks in the GraphLinq IDE are essential components for implementing conditional branching based on integer values. These blocks evaluate the input integer data and determine the appropriate path of execution within the graph based on the specified conditions.
Similar to other branching blocks, the Integer Branch blocks have two main output paths: the True path and the False path. The decision on which path to follow depends on the evaluation of the condition set by the developer. If the condition evaluates to true, the graph will execute the nodes connected to the True output. If the condition evaluates to false, the nodes connected to the False output will be executed.
To set the condition for the Integer Branch, developers can use various comparison operations, such as greater than (">"), less than ("<"), equal to ("=="), not equal to ("!="), greater than or equal to (">="), and less than or equal to ("<="). These operations allow for precise and flexible conditional checks based on the integer inputs.
Example
In this example, we have an Integer Branch block that checks if the input integer value "quantity" is greater than 100. If the condition is true, the graph will execute the nodes connected to the True output, which might perform actions like sending a notification or triggering another process. If the condition is false, the graph will follow the nodes connected to the False output, which might execute different actions based on the quantity value.
The Integer Branch blocks provide developers with the capability to create decision-making logic based on integer values within their graphs. By using conditional checks on integers, developers can build intelligent and adaptable applications that respond to specific numerical conditions. The Integer Branch category is an invaluable tool for developing complex and data-driven graphs in GraphLinq.
More Information
Integer Branch blocks are used to control executive flow by comparing two integer inputs.
Integer Branch blocks are very similar to Decimal Branch blocks; the only difference is that the two numbers being compared are integers, not decimals.
Integer Branch blocks have two input parameters: the two integers we want to compare. They have five yellow output connectors, corresponding to the following five scenarios: the first number is > greater than the second, the first number is >= greater than or equal to the second, the two numbers are == equal, the first number is <= less than or equal to the second, and the first number is < less than the second.
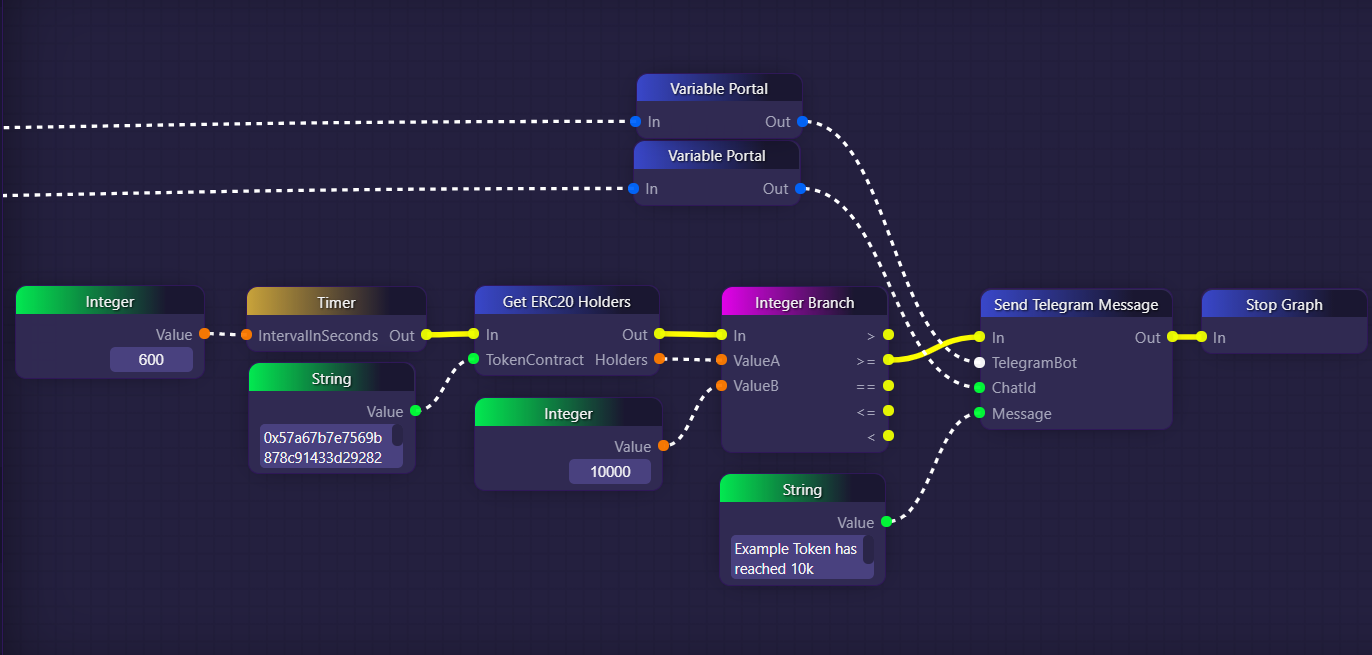
In the example above, we use a Timer block to check how many holders there are for a fictional ERC20 token every ten minutes. We then use an Integer Branch block to check if the amount of holders is greater than or equal to 10,000. If it is, then we use a Telegram bot to send a message about it in what is presumably the Telegram channel for the token's community. After this occurs, we stop the graph, so that it won't continue to say the message every ten minutes.
Last updated
