Boolean
The Boolean block in the GraphLinq IDE is a fundamental building block that represents the Boolean data type, which can have two possible values: "true" or "false". Booleans are commonly used in programming as a means of making decisions and controlling the flow of a program based on certain conditions.
Input Parameters
The Boolean block does not have any inputs. Instead, it serves as a static value block that can be connected to other blocks in a graph.
Output
The Boolean block has one output parameter that represents the Boolean value. This output can be connected to other blocks that accept Boolean values as input.
Usage
The Boolean block is primarily used for making logical decisions within a graph. By connecting the Boolean block's output to a branch or conditional block, developers can control the flow of execution based on whether the value is "true" or "false".
Examples
Using a Boolean for Conditional Branching
Suppose a graph is designed to check whether a user is logged in. The graph might have a login check block that returns a Boolean value indicating whether the user is logged in or not.
Input (Boolean):
trueBased on the output of the login check block (which is "true" in this case), the graph can follow different paths. For example, if the user is logged in (Boolean value is "true"), the graph may proceed to display personalized content. If the user is not logged in (Boolean value is "false"), the graph may redirect the user to the login page.
Using a Boolean for Loop Control
In another scenario, a graph might use a Boolean block to control a loop. For instance, a graph could have a loop that continues to execute as long as a certain condition is true.
Input (Boolean):
When the Boolean value is "false," the loop will terminate, and the graph will proceed to the next set of instructions.
Note: The Boolean block plays a crucial role in decision-making and flow control within graphs. By providing a simple "true" or "false" value, developers can create logic that responds to specific conditions, making their graphs dynamic and responsive to different scenarios. Whether used for conditional branching or loop control, the Boolean block is an essential tool for building versatile and interactive graphs.
More Information
The Boolean block in the GraphLinq IDE allows users to enter boolean values ("true" or "false"), which serve as conditions to determine the execution flow of the graph. These boolean values act as control signals, guiding the graph to follow specific yellow lines based on their true or false status.
A common way to use boolean values to control flow is by employing the Boolean Branch block, which takes a boolean input and executes one of two output connections depending on the value of the boolean. Here's an example of how the Boolean Branch block works:
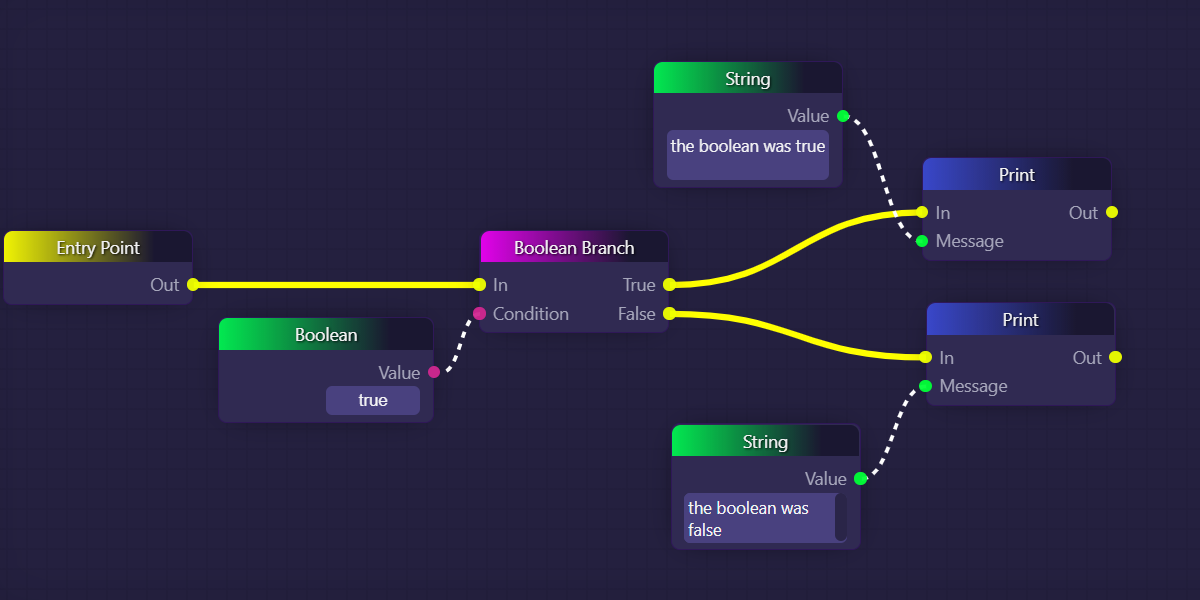
In the above example, "true" has been typed into the Boolean block, which is then being sent as the input data into the Boolean Branch block. When the Boolean Branchblock is run, it will trigger the top yellow connection to fire next, since that output corresponds with the "true" value it received as input. Therefore, the topmost Print block would execute, and we would see "the boolean was true" in our logs.
The example above, while very simple, is not very realistic, because no matter what, the top output of the Boolean Branch will fire every time we run this graph, since we hard-coded its condition to be simply the value "true". The Boolean and Boolean Branch blocks in the above example are therefore pointless.
The following graph snippet is an example of a more realistic use of Boolean and Boolean Branch blocks:
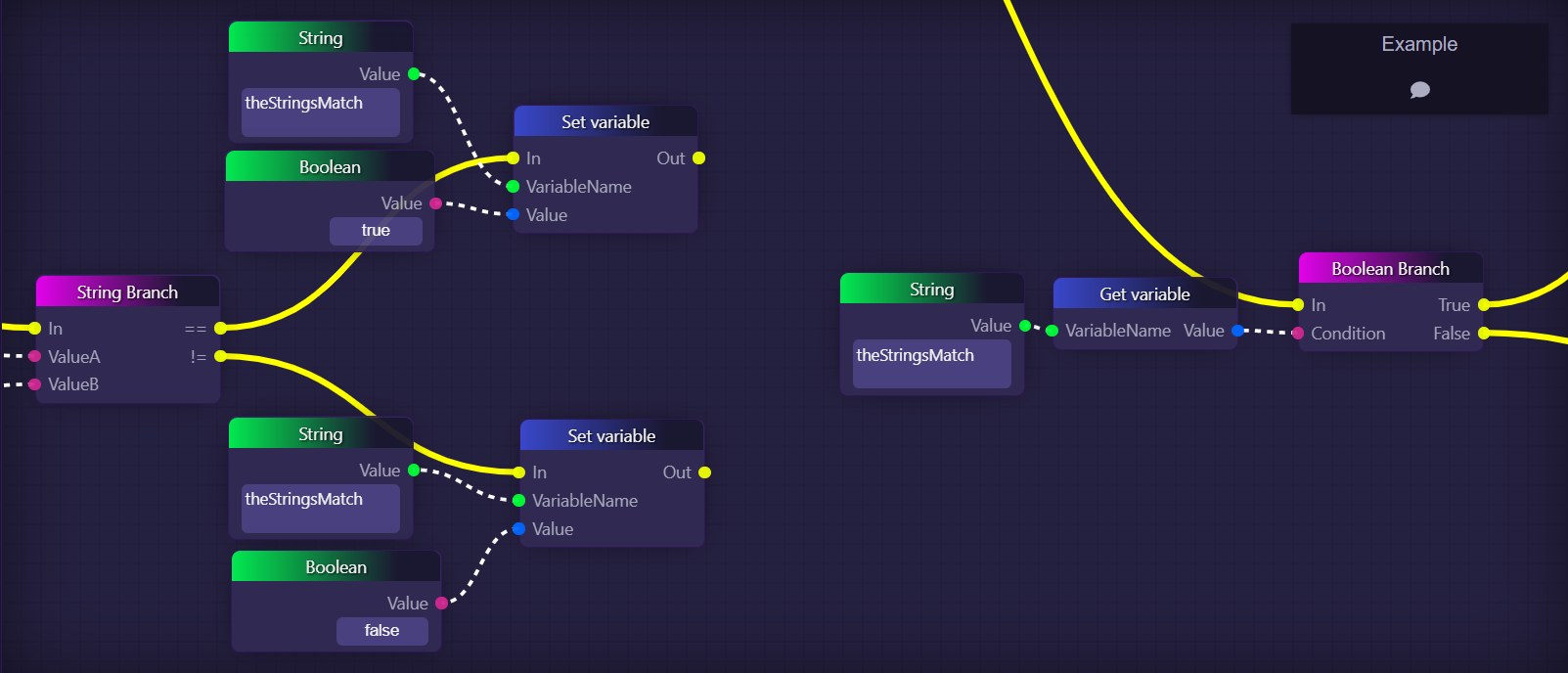
In this example, we are using a String Branch block to check if two given strings are equal. If they are equal, it triggers the top Set variable block, which uses a Booleanblock to assign the value "true" to a variable called "theStringsMatch" (if a variable by that name doesn't exist yet, then this will also declare a variable by that name). If the two strings are not the same, it instead executes the bottom Set variable block, which assigns the value "false" to the same variable.
Later, in the right side of the image, we can see an example of that same boolean variable being accessed with a Get variable block, and the value of that variable is then used as the input to a Boolean Branch block, which will determine which of its outputs will be executed.This is an example of controlling the flow of our graph using a boolean variable whose value is not known to the developer when they make the graph, but is instead calculated only once the graph is running.
Note: the values for Boolean blocks are not case-sensitive, so they work with "true", "True", "false", and "False". If you were to type anything besides those values into the Boolean block above, then neither of the Boolean Branch outputs would execute.
Last updated
