Percentage Difference
Calculate the percentage difference between two numeric values
The Percentage Difference block in the GraphLinq IDE is a powerful mathematical tool used to calculate the percentage difference between two numeric values. This block is particularly useful for analyzing data changes, comparing variations between values, and assessing relative differences in quantities.
Block Description
The Percentage Difference block belongs to the Math blocks category in the GraphLinq IDE. Like other blocks in this category, it is a non-executive block, meaning it does not have yellow connectors and is implicitly called when its output is needed by other blocks during graph execution.
Input Parameters
The Percentage Difference block requires two input parameters:
A (Numeric Type): The A input represents the initial numeric value that serves as the baseline for comparison.
B (Numeric Type): The B input is the second numeric value, which will be compared to the baseline value to calculate the percentage difference.
Both A and B inputs can accept various numeric data types, including decimals, integers, and longs. The block automatically handles type conversion if the two inputs have different numeric data types.
Output
The Percentage Difference block outputs the percentage difference between values A and B. The output is a decimal value representing the percentage change. The output can be positive or negative, indicating whether the value B is an increase or decrease relative to the baseline value A.
Example Use Case
Let's explore a practical example of how the Percentage Difference block can be utilized in a graph:
The graph retrieves historical stock prices for a particular company and stores them in variables A and B.
The Percentage Difference block is invoked, taking the historical stock price (A) as the baseline and the current stock price (B) as the second value.
The block calculates the percentage difference between the historical price and the current price, indicating the price variation.
The output represents the percentage change in the stock price over the selected period.
In this example, the Percentage Difference block enables the graph to analyze and visualize the percentage change in the stock price, aiding investors and analysts in making informed decisions based on historical data.
The Percentage Difference block is a valuable mathematical tool within the GraphLinq IDE, facilitating the calculation of percentage changes between two numeric values. Its versatility makes it ideal for a wide range of applications, including data analysis, financial modeling, and trend assessment. By employing the Percentage Difference block, developers can easily assess and understand the relative differences between quantities, providing valuable insights in their graphs.
More Information
The Percentage Difference block in the GraphLinq IDE is a valuable tool for calculating the percentage difference between two given numeric values "A" and "B." It enables developers to determine the percentage change or variance between two quantities, expressing the result as a percentage. The Percentage Difference block plays a crucial role in various scenarios where comparing relative changes in values is essential.
Block Details
The Percentage Difference block takes two input parameters, "A" and "B," which represent the numeric values for comparison. Both "A" and "B" can be of various numeric data types, such as decimal, integer, or long. The block calculates the percentage difference between "A" and "B" and provides the result as its output.
Execution
As with other block types in the Math category, the Percentage Difference block is non-executive. It does not have yellow connectors and is implicitly called whenever its output is needed as input by other executing blocks. When the Percentage Difference block's output is required in a graph, it performs the calculation to find the percentage difference between the input values "A" and "B" and delivers the result as its output.
Use Case
The Percentage Difference block finds broad applications in various fields, including finance, economics, statistics, and data analysis. In finance, it is used to analyze the performance of investments and financial instruments by comparing their values over time. In economics, it aids in evaluating changes in economic indicators and trends. In statistics, it is utilized to assess changes in data distributions and relationships between variables. In data analysis, the block helps in quantifying variations in datasets and identifying outliers.
Example
Let's consider an example to illustrate the usage of the Percentage Difference block. Suppose we have a graph that tracks the monthly revenue of an e-commerce website. The graph takes the revenue for the current month (A) and the revenue for the previous month (B) as inputs and needs to calculate the percentage change in revenue.
To achieve this, we can use the Percentage Difference block. By providing the revenue for the current month (A) and the revenue for the previous month (B) to the Percentage Difference block, it calculates the percentage difference and outputs the result. This enables us to quickly determine the percentage increase or decrease in revenue from one month to the next, providing valuable insights into the business's performance.
The Percentage Difference block's ability to calculate percentage variations is crucial in various real-world scenarios where understanding relative changes in values is essential. It empowers developers to perform percentage-based analyses within their graphs and facilitates data-driven decision-making in diverse domains.
Full Example
Percentage Difference blocks calculate the percentage difference between two given numbers, with respect to the first of the two numbers.
Percentage Difference blocks have two input parameters called "A" and "B". Their output expresses what percent "A" would need to change for it to be equal to "B". This is equivalent to 100(B - A) / A.
As with all block types in the Math category, Percentage Difference blocks are non-executive blocks, which means that they have no yellow connectors, and thus they are never called explicitly by other blocks, and they themselves cannot call other blocks. Instead, they are called implicitly whenever their output is required as input by some other block that is executing. We can observe this happening in the example below.
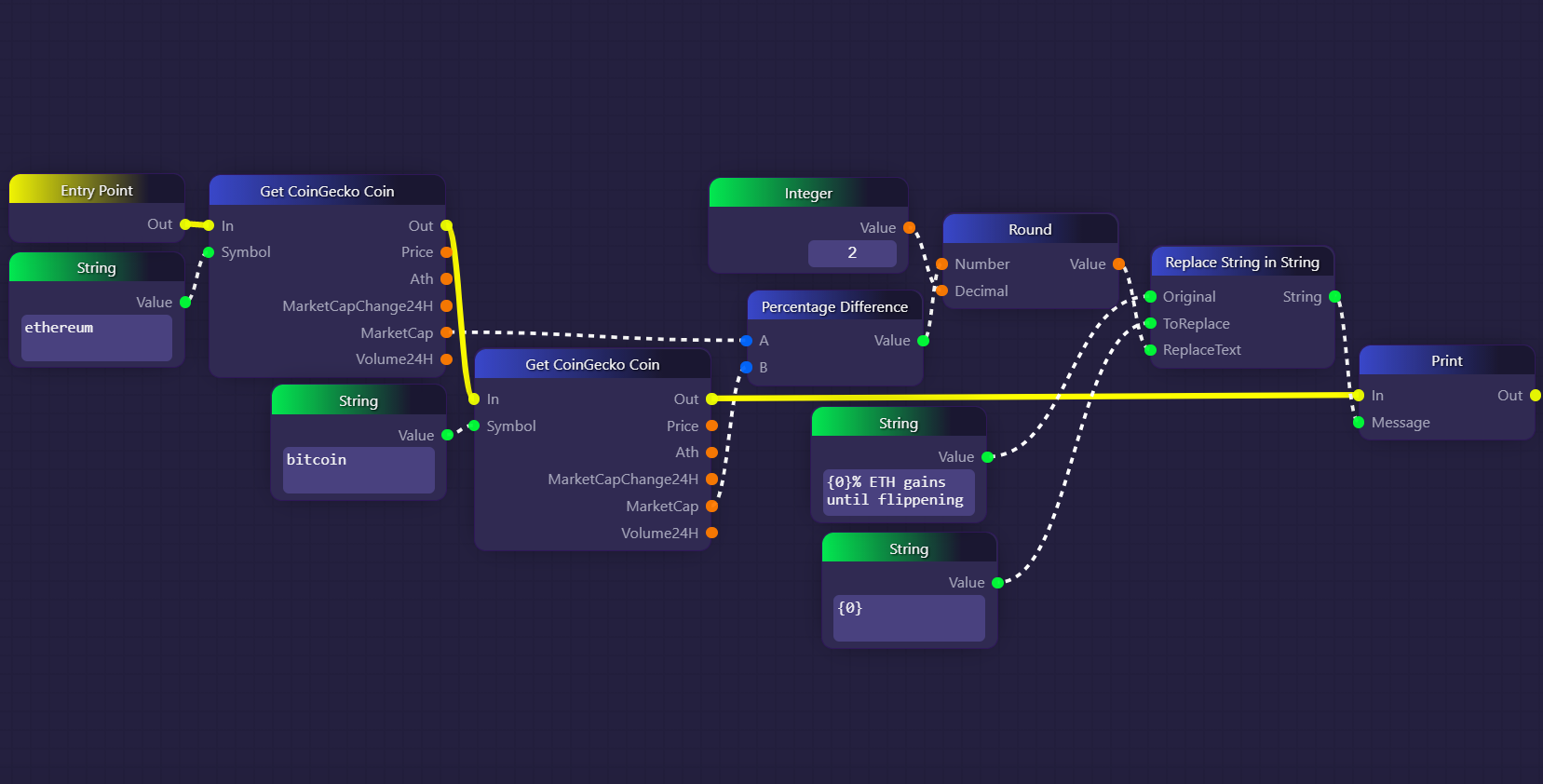
In the example above, we use a Percentage Difference block to compare the market capitalizations of ETH and BTC in order to calculate what percentage ETH needs to gain before it flips BTC's market cap.
When the graph starts, we use a sequence of two Get CoinGecko Coin blocks to retrieve the market capitalizations of ETH and BTC, and we then feed these market cap values into the Percentage Difference block. Note that we link up ETH as "A" and BTC as "B", which means that the output will be the percentage change Ether needs to undergo to reach Bitcoin's market cap, rather than the other way around.
After calculating our percentage difference, we pass that value to a Round block in order to format it into a more displayable form, and then we pack it into a short message using a Replace String In String block. Finally, we record that message in the graph's logs using a Print block.
In our example, we simply calculate and then print the percentage difference between ETH and BTC market caps one time, right when the graph starts running. It is easy to imagine a more robust and complete example in which this calculation is done whenever requested by users on some platform like Discord or Telegram.
Last updated
