Boolean Branch
The Boolean Branch blocks in the GraphLinq IDE are essential tools for implementing conditional branching based on boolean values. These blocks allow developers to make decisions in the graph's execution flow based on the outcome of boolean expressions.
A Boolean Branch block has two primary output paths: the True path and the False path. The decision on which path to follow depends on the result of the boolean condition set by the developer. If the condition evaluates to true, the graph will execute the nodes connected to the True output. Conversely, if the condition evaluates to false, the nodes connected to the False output will be executed.
Developers can set the conditions for the Boolean Branch using various logical operations such as AND, OR, and NOT. These operations allow for combining multiple boolean values and creating complex conditional expressions. The ability to use logical operations gives developers the flexibility to design intricate logic based on boolean inputs.
Example
In this example, we have a Boolean Branch block that checks two boolean conditions: "isUserLoggedIn" and "hasPurchasedItem." The graph will execute the nodes connected to the True output if both conditions are true, indicating that the user is logged in and has made a purchase. If either condition is false, the graph will follow the nodes connected to the False output, which might handle scenarios for non-logged-in users or users who have not made a purchase.
The Boolean Branch blocks enable developers to create dynamic and adaptive graphs that respond to specific boolean conditions. By leveraging logical operations, developers can build powerful decision-making mechanisms within their graphs, making them capable of handling complex scenarios based on boolean inputs. The Boolean Branch category empowers developers to build intelligent applications that react intuitively to boolean conditions in GraphLinq.
More Information
Boolean Branch blocks are used to control the executive flow (which yellow connection will fire next) based upon the value of a boolean variable.
Boolean Branch blocks have one input parameter, which is the boolean that will determine the output. While it is possible to provide this boolean input as an actual Boolean block that has had "true" or "false" typed into it, there wouldn't be much point to this, as the Boolean Branch block would always fire in the exact same way, since the input has been typed in as a fixed value (equivalent to using a boolean literal in programming).
It makes more sense to provide the input to a Boolean Branch block using a Get variable block that retrieves the value of a boolean variable that was previously declared with a Set variable block. In this way, we can use Boolean Branch blocks to determine paths of execution based upon the values of boolean variables.
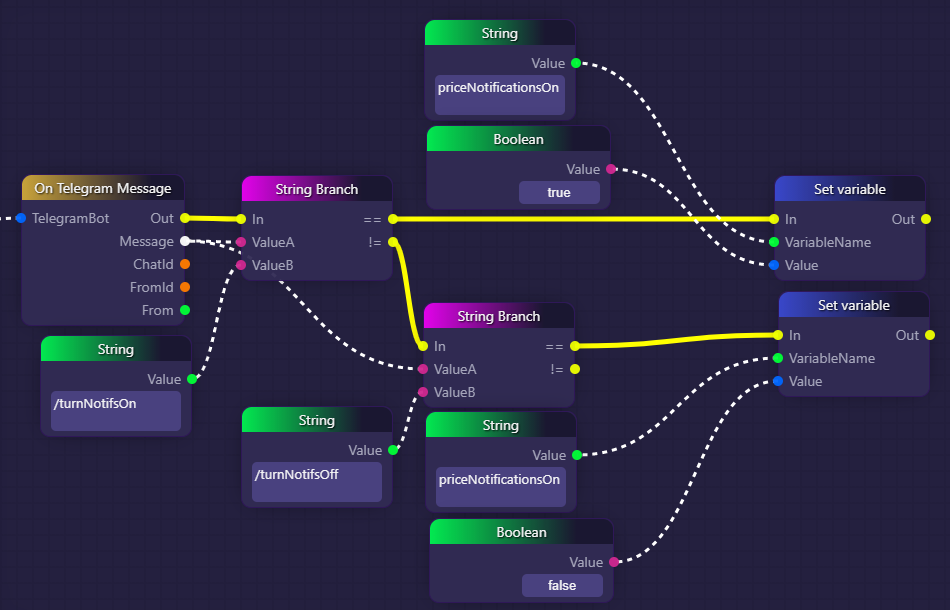
The following example is in two parts, but they are part of the same graph. The goal here is to allow Telegram users to use commands to turn a notification bot on and off. The bot outputs the price of Bitcoin in a Telegram channel every 60 seconds when it is on.
In the first part, we are listening to Telegram messages that are picked up by our Telegram bot. For each message heard, we are using String Branch blocks to check whether the message equals "/turnNotifsOn" or "/turnNotifsOff". If either of these strings are detected then we use Set variable blocks to set the value of a variable called "priceNotificationsOn" to "true" or "false", respectively.
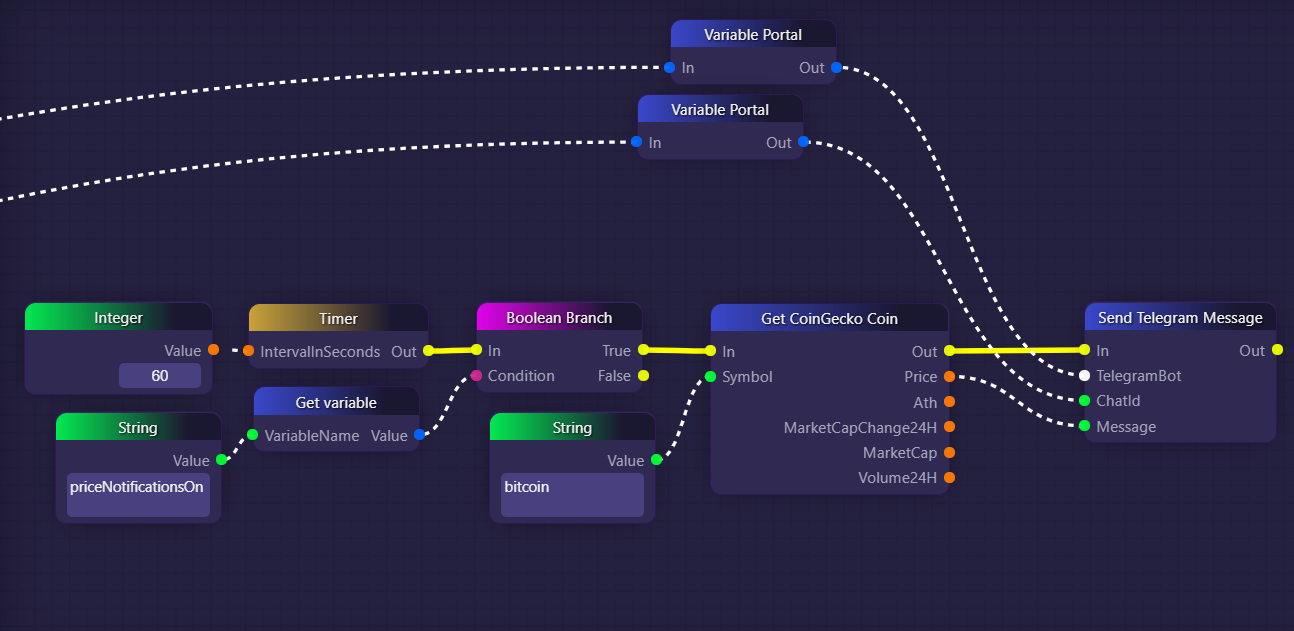
In the second part of the example, we have a Timer block that fires every minute. Whenever it fires, we execute a Boolean Branch block. We use a Get variable block to access the value of the variable called "priceNotificationsOn" (the same variable that Telegram users are able to set thanks to the first part of our example). If the value of "priceNotificationsOn" is "true", then the Boolean Branch will trigger the Get CoinGecko Coin block, and we will end up outputting the price of Bitcoin into the Telegram channel. Otherwise, nothing will happen, and we will reevaluate in 60 seconds when the Timer block fires again.
The Boolean Branch block in the GraphLinq IDE is used to control the flow of execution based on a boolean condition. It has two inputs and two outputs, all represented by yellow lines in the IDE. The first input is the path of execution, and the second input is a boolean variable called "Condition".
The Boolean Branch block reads the value of the "Condition" boolean variable and follows the yellow execution path based on its true or false status. If the "Condition" is true, the Boolean Branch will follow the "True" output yellow line, and if the "Condition" is false, it will follow the "False" output yellow line.
Last updated
