Ceiling
Round a numeric value up to the nearest integer greater than or equal to the original value
The Ceiling block in the GraphLinq IDE is a powerful mathematical tool used to round a numeric value up to the nearest integer greater than or equal to the original value. This block is particularly useful when precision is not required, and developers need to ensure that a value is always rounded up to the nearest whole number or integer.
Block Description
The Ceiling block is categorized under the Math blocks in the GraphLinq IDE. Like other blocks in this category, it is a non-executive block, meaning it does not have yellow connectors and is implicitly called whenever its output is needed as input by other blocks during graph execution.
Input Parameter
The Ceiling block requires one input parameter:
A (Numeric Type): The A input represents the numeric value that needs to be rounded up to the nearest integer.
The A input can accept various numeric data types, such as decimals, integers, and longs.
Output
The Ceiling block outputs the result of rounding up the input value A to the nearest integer greater than or equal to A. The output is of the same data type as the input value.
Example Use Case
Let's explore a practical example of how the Ceiling block can be used within a graph to ensure that a calculated value is always rounded up to the nearest whole number.
The graph performs various complex calculations, resulting in a numeric value (e.g., 34.75, 11.35, etc.).
The Ceiling block is called, taking the calculated numeric value as input A.
The block rounds up the value to the nearest integer greater than or equal to the original value.
The resulting rounded-up value (e.g., 35, 12) is further used in subsequent calculations or to display data in the graph's output.
In this example, the Ceiling block ensures that the calculated numeric value is always rounded up to the nearest whole number, even if the original value contains decimal places. This rounding behavior can be beneficial in various scenarios, such as calculating quantities for inventory management, displaying rounded data in user interfaces, or ensuring proper billing amounts in financial applications.
Conclusion
The Ceiling block provides a straightforward and effective solution for rounding numeric values up to the nearest integer in the GraphLinq IDE. By using this block, developers can ensure that a value is always rounded up, regardless of its decimal precision. Whether it's for simplifying complex calculations or ensuring data consistency, the Ceiling block proves to be a valuable tool in achieving precise and predictable rounding outcomes.
More Information
The Ceiling block in the GraphLinq IDE is a powerful mathematical tool used to round up a numeric value to the nearest integer greater than or equal to that value. This block is particularly useful when precision is required in numeric calculations, ensuring that values are rounded up to the desired level of accuracy.
Block Details
The Ceiling block takes a single input parameter, "A," which represents the numeric value that needs to be rounded up. This input can accept various types of numeric data, such as decimal, integer, or long. The Ceiling block's output is the rounded-up integer result of the input value.
Execution
Like other block types in the Math category, the Ceiling block is a non-executive block. It does not have yellow connectors and is not directly called by other blocks. Instead, it is implicitly called whenever its output is required as input by other executing blocks.
Use Case
The Ceiling block is essential in situations where precise rounding of numeric values is required. It is commonly used in financial applications, pricing calculations, and scenarios where data needs to be presented in a clear and consistent format. For example, in e-commerce applications, the Ceiling block can be used to round up product prices to the nearest whole number or a specific decimal place, ensuring consistent and accurate pricing.
Example
Let's consider an example to demonstrate the functionality of the Ceiling block. Suppose we have a graph that calculates the total cost of purchasing a specific quantity of items. The graph takes inputs "Unit Price" and "Quantity," representing the price of each item and the desired quantity to purchase, respectively.
To determine the total cost, we need to multiply the unit price by the quantity. However, in certain scenarios, the unit price may have decimal places, and we want to ensure that the total cost is rounded up to the nearest whole number. Here, we can use the Ceiling block to round up the calculated total cost.
The Ceiling block takes the product of the unit price and quantity as input and rounds it up to the nearest integer, representing the total cost of the purchase. This ensures that the total cost is always rounded up to the desired level of accuracy, even if the unit price has fractional values.
By utilizing the Ceiling block, developers can perform precise rounding of numeric values within their graphs, ensuring that calculations and data processing tasks are accurate and reliable. The Ceiling block is an essential tool for maintaining consistency and precision in numerical operations, making it a valuable asset in various applications across industries.
Full Example
Ceiling blocks are used to round numbers up to the nearest integer. They are very similar to Floor blocks; the only difference between the two is that Ceiling blocks round up (so 5.01 -> 6), whereas Floor blocks round down (so 5.99 -> 5).
Ceiling blocks only have one input parameter called "Number", which is the number that we would like to round up. The logical data type for this parameter is decimal.
As with all block types in the Math category, Ceiling blocks are non-executive blocks, which means that they have no yellow connectors, and thus they are never called explicitly by other blocks, and they themselves cannot call other blocks. Instead, they are called implicitly whenever their output is required as input by some other block that is executing. We can observe this happening in the example below.
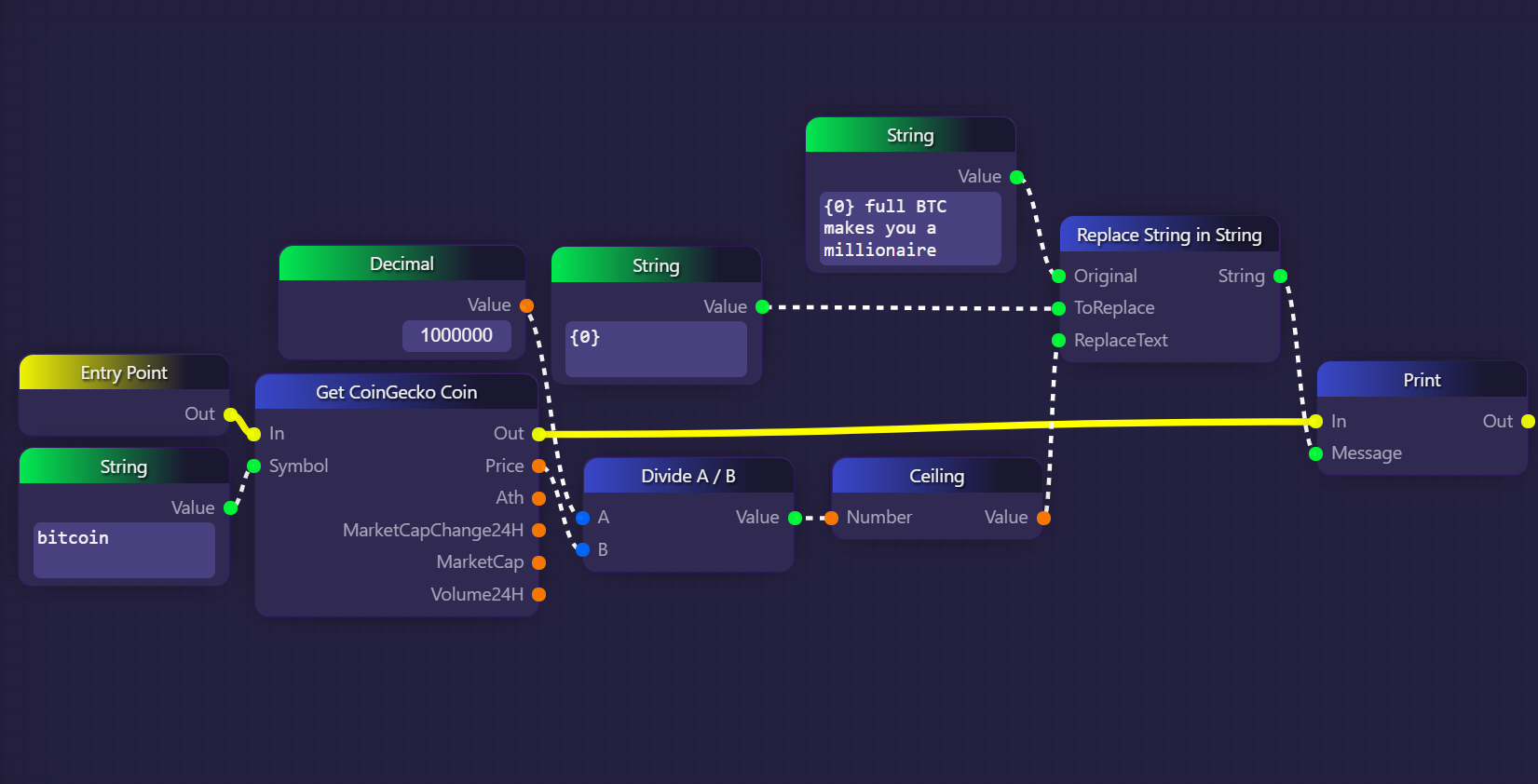
In the example above, we are simply calculating and printing the lowest amount of entire Bitcoins worth at least $1 million at the current market price as per CoinGecko.
We use a Get CoinGecko Coin block to fetch the price of Bitcoin once when the graph begins its execution. We then divide 1 million by the current price of Bitcoin using a Divide A / B block. This gives us the true amount of Bitcoin which is equivalent to $1 million dollars. For example, if BTC currently costs $35,000, this calculation would result in 28.57 BTC. However, we want the lowest amount of the whole BTC worth at least $1 million, which is where our Ceiling block comes in. Once we ceiling this value, we get 29, which is then packed into a short message using a Replace String In String block, and recorded in the graph's logs with a Print block.
Note that the yellow executive output on the Get CoinGecko Coin block is plugged directly into the Print block, which means that this is the next block to be called after the Get CoinGecko Coin block. However, for the Print block to execute, its "Message" parameter must be supplied with a value. This causes the Replace String In Stringblock to resolve, which in turn causes the Ceiling block to resolve (which then causes the Divide A / B block to resolve). This is an example of implicit calling, where a non-executive block is called only when its output is required by some other block's input.
Last updated
