Secret String
Secret String blocks are functionally equivalent to regular String blocks in that both of these block types serve to allow the graph developer to enter string data into the graph.
The Secret String block is used to securely store sensitive data, such as API keys or passwords, within the graph's data context. Unlike regular String blocks, the contents of Secret String blocks are hidden from view to maintain security and privacy.
The difference is that the contents of Secret String blocks are hidden, like "••••••••••". They also cannot be copied to the clipboard.
This is useful when building graphs that others will have access to that contain sensitive information, like a Discord account token or a Binance API secret key.
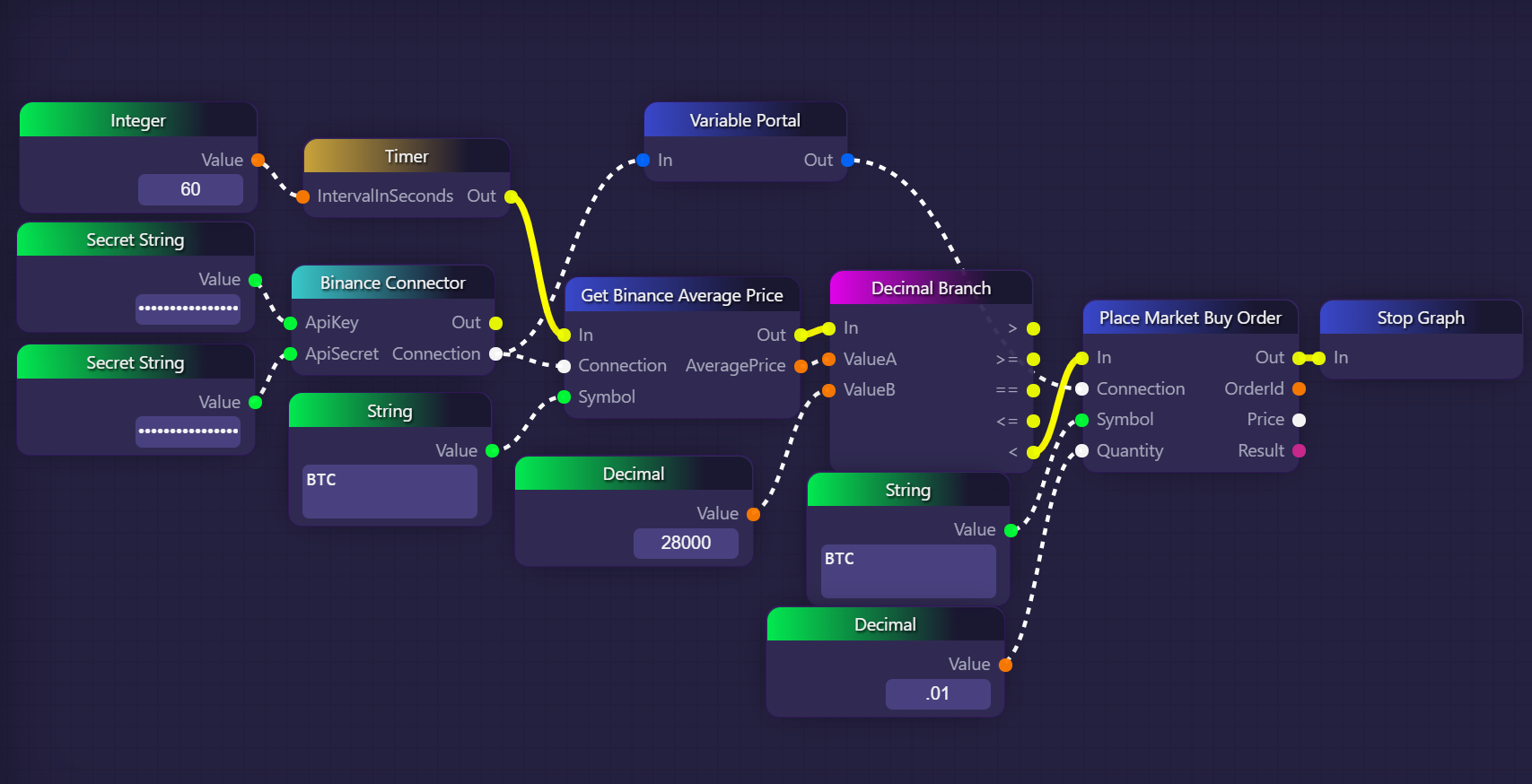
In the example above, we use a Timer block to check the price of Bitcoin on Binance once every minute. We then use a Decimal Branch block to check if the price is below $28,000; if it is, we place a market buy order for 1% of a Bitcoin with a Place Market Buy Order block, and then we terminate execution with a Stop Graph block.
The Secret String blocks are used here when setting up the Binance Connector block with its API key inputs. We could have used regular String blocks here, but since Binance API keys are sensitive (especially the "ApiSecret" parameter) it makes sense to secure our graph by using Secret String blocks. This way, having access to this graph file isn't equivalent to knowing our Binance access credentials.
The Secret String block is essential for protecting confidential data within the graph, keeping it hidden from prying eyes and potential security threats.
Last updated
