Divide A / B
Perform division operations
The Divide A / B block in the GraphLinq IDE is a fundamental mathematical block used to calculate the result of dividing one numeric value (A) by another (B). This block enables developers to perform division operations within their graphs and handle scenarios where sharing or splitting quantities is required.
Block Description
The Divide A / B block belongs to the Math blocks category in the GraphLinq IDE. As with other blocks in this category, it is a non-executive block, meaning it lacks yellow connectors and is implicitly called when its output is needed as input by other blocks during graph execution.
Input Parameters
The Divide A / B block requires two input parameters:
A (Numeric Type): The A input represents the numerator or dividend in the division operation.
B (Numeric Type): The B input represents the denominator or divisor in the division operation.
Both A and B inputs accept various numeric data types, such as decimals, integers, and longs. It is essential to ensure that the B input is not set to zero, as division by zero is undefined and may lead to errors in the graph's execution.
Output
The Divide A / B block outputs the result of dividing the value of input A by the value of input B. The output is of the same data type as the inputs and represents the quotient or result of the division operation.
Example Use Case
Let's explore a practical example of how the Divide A / B block can be utilized within a graph to calculate the division of two quantities:
The graph retrieves data, such as the total quantity of items in stock (A) and the number of items sold (B).
The Divide A / B block is called, taking the values of A (total quantity) and B (number of items sold) as inputs.
The block calculates the division of A by B, resulting in the ratio of items sold to the total quantity.
The resulting quotient is then used for further analysis or to generate reports on sales performance.
In this example, the Divide A / B block facilitates the computation of a vital business metric—the percentage of items sold out of the total quantity available. This information can be crucial for inventory management, sales forecasting, and decision-making processes.:
Conclusion
The Divide A / B block is an indispensable tool for performing division operations within graphs in the GraphLinq IDE. By using this block, developers can effortlessly calculate ratios, proportions, or percentages based on numeric values. Whether it's for business analytics, financial calculations, or any scenario that requires division, the Divide A / B block proves to be a valuable asset in ensuring accurate and efficient mathematical computations.
More Information
The Divide A / B block in the GraphLinq IDE is a fundamental mathematical block used to perform division operations between two numeric values. This block enables developers to divide one number (A) by another number (B) and obtain the result as the output.
Block Details
The Divide A / B block has two input parameters: "A" and "B." These parameters represent the dividend and divisor, respectively. The block takes the value of "A" and divides it by the value of "B" to compute the division result. Both "A" and "B" can be of various numeric data types, such as decimal, integer, or long.
Execution
As with other block types in the Math category, the Divide A / B block is non-executive. It does not have yellow connectors and is not explicitly called by other blocks. Instead, it is implicitly called whenever its output is needed as input by other executing blocks.
Use Case
The Divide A / B block is essential for performing division operations within graphs. It finds applications in various scenarios, such as calculating ratios, proportions, percentages, and scaling values. In financial applications, it can be used to determine unit prices, interest rates, or profit margins. Additionally, the block is valuable in data analysis and manipulation tasks where numeric values need to be divided to obtain meaningful insights.
Example
Let's consider an example to illustrate the functionality of the Divide A / B block. Suppose we have a graph that calculates the average rating of a product based on the total sum of ratings and the number of ratings received.
The graph takes inputs "Total Ratings" (A) and "Number of Ratings" (B). To calculate the average rating, we need to divide the total sum of ratings by the number of ratings received. Here, we can use the Divide A / B block to perform the division operation.
The block takes "Total Ratings" as A and "Number of Ratings" as B, and it computes the division result, which represents the average rating of the product. This enables us to obtain the average rating as output, which can then be used for further analysis or display.
By using the Divide A / B block, developers can perform precise division operations within their graphs, allowing them to handle various numerical calculations and data processing tasks efficiently. The block plays a crucial role in ensuring accuracy and reliability in division-based computations, making it an indispensable component in numerous applications.
Full Example
Divide A / B blocks divide one given number by another and then output the result.
Divide A / B blocks have two input parameters called "A" and "B". These are the two numbers that we want to get the quotient of. Note that these input parameters can be supplied with any type of numeric data (decimal, integer, long), and the two data types do not need to match (ie: you can divide a decimal value by an integer value).
As with all block types in the Math category, Divide A / B blocks are non-executive blocks, which means that they have no yellow connectors, and thus they are never called explicitly by other blocks, and they themselves cannot call other blocks. Instead, they are called implicitly whenever their output is required as input by some other block that is executing. We can observe this happening in the example below.
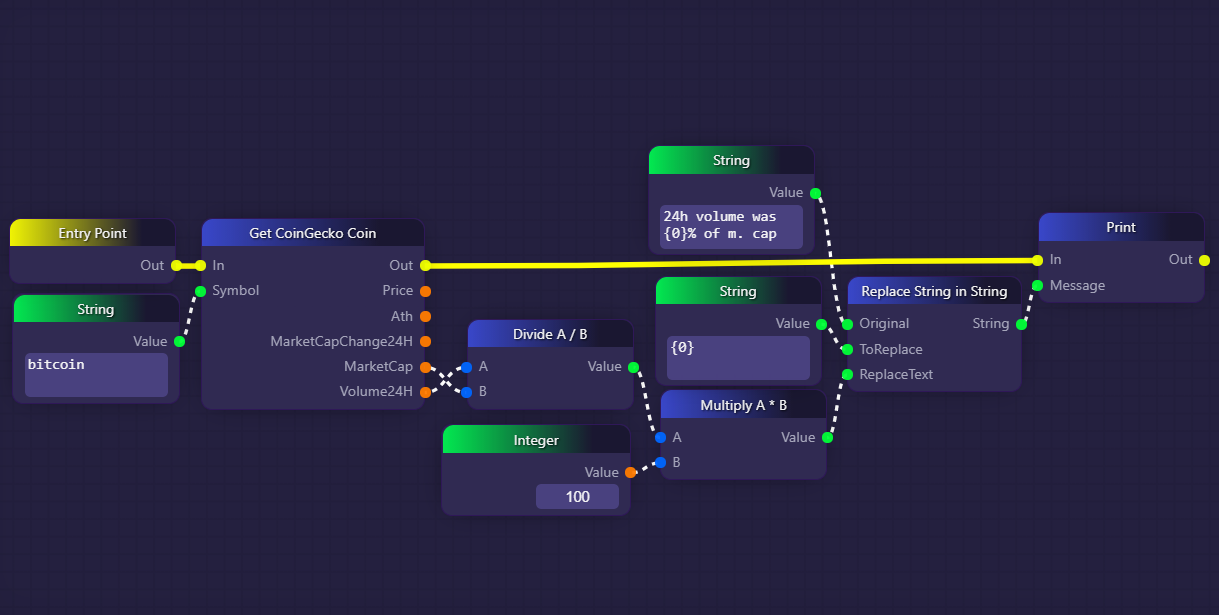
In this example, we are calculating the 24-hour volume of Bitcoin as a percentage of its market capitalization. After using a Get CoinGecko Coin block to access current statistics about Bitcoin, we use our Divide A / B block to divide Bitcoin's 24-hour trade volume with its market cap to get the ratio between them, which is the first step in calculating a percentage. We then use a Multiply A * B block to multiply this ratio by 100, which is the second and final step in calculating a percentage.
Once we have calculated the percentage, we use a Replace String In String block to construct a short message including our result, and then print it into the graph's logs using a Print block.
Note that the yellow executive output on the Get CoinGecko Coin block is plugged directly into the Print block, which means that this is the next block to be called after the Get CoinGecko Coin block. However, for the Print block to execute, its "Message" parameter must be supplied with a value. This causes the Replace String In Stringblock to resolve, which in turn causes the Multiply A * B block to resolve, which finally causes our Divide A / B block to resolve. This is an example of implicit calling, where a non-executive block is called only when its output is required by some other block's input.
In our example, we simply calculate and then print Bitcoin trade volume as a percentage of market cap one time, right when the graph starts running. It is easy to imagine a more advanced and utile example in which this calculation is done whenever requested by users on some platform like Discord or Telegram.
Last updated
